World Atlas: Ukraine. On this page you can see the map, country flag and many detailed information about the people, history and economy of Ukraine.
Here you can find online selected information about the geography, inhabitants, government, economy and history of Ukraine. Included are selected statistics, an overview map and the detailed map of Ukraine. But let's start with the flag of Ukraine here:
Ukraine - Overview:
What you should know about Ukraine? Let's start with this: Ukraine was the center of the first eastern Slavic state, Kyivan Rus, which during the 10th and 11th centuries was the largest and most powerful state in Europe. Weakened by internecine quarrels and Mongol invasions, Kyivan Rus was incorporated into the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and eventually into the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The cultural and religious legacy of Kyivan Rus laid the foundation for Ukrainian nationalism through subsequent centuries. A new Ukrainian state, the Cossack Hetmanate, was established during the mid-17th century after an uprising against the Poles. Despite continuous Muscovite pressure, the Hetmanate managed to remain autonomous for well over 100 years. During the latter part of the 18th century, most Ukrainian ethnographic territory was absorbed by the Russian Empire. Following the collapse of czarist Russia in 1917, Ukraine achieved a short-lived period of independence (1917-20), but was reconquered and endured a brutal Soviet rule that engineered two forced famines (1921-22 and 1932-33) in which over 8 million died. In World War II, German and Soviet armies were responsible for 7 to 8 million more deaths. Although Ukraine achieved independence in 1991 with the dissolution of the USSR, democracy and prosperity remained elusive as the legacy of state control and endemic corruption stalled efforts at economic reform, privatization, and civil liberties. A peaceful mass protest referred to as the "Orange Revolution" in the closing months of 2004 forced the authorities to overturn a rigged presidential election and to allow a new internationally monitored vote that swept into power a reformist slate under Viktor Yushchenko. Subsequent internal squabbles in the Yushchenko camp allowed his rival Viktor Yanukovych to stage a comeback in parliamentary (Rada) elections, become prime minister in August 2006, and be elected president in February 2010. In October 2012, Ukraine held Rada elections, widely criticized by Western observers as flawed due to use of government resources to favor ruling party candidates, interference with media access, and harassment of opposition candidates. President Yanukovych's backtracking on a trade and cooperation agreement with the EU in November 2013 - in favor of closer economic ties with Russia - and subsequent use of force against students, civil society activists, and other civilians in favor of the agreement led to a three-month protest occupation of Kyiv's central square. The government's use of violence to break up the protest camp in February 2014 led to all out pitched battles, scores of deaths, international condemnation, and the president's abrupt departure for Russia. New elections in the spring allowed pro-West president Petro Poroshenko to assume office on 7 June 2014. Shortly after Yanukovych's departure in late February 2014, Russian President Putin ordered the invasion of Ukraine's Crimean Peninsula claiming the action was to protect ethnic Russians living there. Two weeks later, a "referendum" was held regarding the integration of Crimea into the Russian Federation. The "referendum" was condemned as illegitimate by the Ukrainian Government, the EU, the US, and the UN General Assembly (UNGA). In response to Russia's purported annexation of Crimea, 100 members of the UN passed UNGA resolution 68/262, rejecting the "referendum" as baseless and invalid and confirming the sovereignty, political independence, unity, and territorial integrity of Ukraine. Russia also continues to supply so-called separatists in two of Ukraine's eastern provinces with manpower, funding, and materiel resulting in an armed conflict with the Ukrainian Government. Representatives from Ukraine, Russia, and the unrecognized separatist republics signed the Minsk Protocol and Memorandum in September 2014 to end the conflict. However, this agreement failed to stop the fighting. In a renewed attempt to alleviate ongoing clashes, leaders of Ukraine, Russia, France, and Germany negotiated a follow-on package of measures in February 2015 to implement the Minsk Agreements. Representatives from Ukraine, Russia, and the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe also meet regularly to facilitate implementation of the peace deal. More than 33,000 civilians have been killed or wounded in the fighting resulting from Russian aggression in eastern Ukraine.
Geography of Ukraine
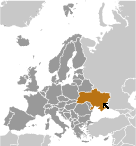 Where on the globe is Ukraine? The location of this country is Eastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea, between Poland, Romania, and Moldova in the west and Russia in the east. Total area of Ukraine is 603,550 sq km, of which 579,330 sq km is land. So this is quite a large country. How could we describe the terrain of the country? This way: mostly fertile plains (steppes) and plateaus, with mountains found only in the west (the Carpathians) or in the extreme south of the Crimean Peninsula. The lowest point of Ukraine is Black Sea 0 m, the highest point Hora Hoverla 2,061 m. And the climate is temperate continental; Mediterranean only on the southern Crimean coast; precipitation disproportionately distributed, highest in west and north, lesser in east and southeast; winters vary from cool along the Black Sea to cold farther inland; warm summers across the greater part of the country, hot in the south.
Where on the globe is Ukraine? The location of this country is Eastern Europe, bordering the Black Sea, between Poland, Romania, and Moldova in the west and Russia in the east. Total area of Ukraine is 603,550 sq km, of which 579,330 sq km is land. So this is quite a large country. How could we describe the terrain of the country? This way: mostly fertile plains (steppes) and plateaus, with mountains found only in the west (the Carpathians) or in the extreme south of the Crimean Peninsula. The lowest point of Ukraine is Black Sea 0 m, the highest point Hora Hoverla 2,061 m. And the climate is temperate continental; Mediterranean only on the southern Crimean coast; precipitation disproportionately distributed, highest in west and north, lesser in east and southeast; winters vary from cool along the Black Sea to cold farther inland; warm summers across the greater part of the country, hot in the south.
Inhabitants of Ukraine
Let's take a look how many people live in Ukraine. The number is: 44,033,874 (July 2017 est.). So quite a lot people live here. Who lives here? Ukrainian 77.8%, Russian 17.3%, Belarusian 0.6%, Moldovan 0.5%, Crimean Tatar 0.5%, Bulgarian 0.4%, Hungarian 0.3%, Romanian 0.3%, Polish 0.3%, Jewish 0.2%, other 1.8% (2001 est.). What are the languages in Ukraine? Ukrainian (official) 67.5%, Russian (regional language) 29.6%, ther (includes small Crimean Tatar-, Moldovan/Romanian-, and Hungarian-speaking minorities) 2.9% (2001 est.). And the religions: Orthodox (includes Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox (UAOC), Ukrainian Orthodox - Kyiv Patriarchate (UOC-KP), Ukrainian Orthodox - Moscow Patriarchate (UOC-MP)), Ukrainian Greek Catholic, Roman Catholic, Protestant, Muslim, Jewish. How old are the people in average? 40.6 years. We have to add that this number is the median - so one half of the people is older than this, one half is younger. And what is their life expectancy (at birth)? This: 72.1 years. Where the people live in Ukraine? Here: densest settlement in the eastern (Donbas) and western regions; noteable concentrations in and around major urban areas of Kyiv, Kharkiv, Donets'k, Dnipropetrovs'k, and Odesa. The major urban areas of Ukraine are: KYIV (capital) 2.942 million; Kharkiv 1.441 million; Odesa 1.01 million; Dnipropetrovsk 957,000; Donetsk 934,000; Zaporizhzhya 753,000 (2015).
Government and Economy of Ukraine
The capital of Ukraine is Kyiv (Kiev) and the government type semi-presidential republic. Let's take a look at the administrative divisions - 24 provinces (oblasti, singular - oblast'), 1 autonomous republic (avtonomna respublika), and 2 municipalities (mista, singular - misto) with oblast status; Cherkasy, Chernihiv, Chernivtsi, Crimea or Avtonomna Respublika Krym (Simferopol'), Dnipropetrovs'k (Dnipro), Donets'k, Ivano-Frankivs'k, Kharkiv, Kherson, Khmel'nyts'kyy, Kirovohrad (Kropyvnyts'kyy), Kyiv, Kyiv, Luhans'k, L'viv, Mykolayiv, Odesa, Poltava, Rivne, Sevastopol', Sumy, Ternopil', Vinnytsya, Volyn' (Luts'k), Zakarpattya (Uzhhorod), Zaporizhzhya, Zhytomy. Regarding the economy of Ukraine, important industrial products are coal, electric power, ferrous and nonferrous metals, machinery and transport equipment, chemicals, food processing. Important agricultural products are grain, sugar beets, sunflower seeds, vegetables; beef, milk. The most important export commodities are ferrous and nonferrous metals, fuel and petroleum products, chemicals, machinery and transport equipment, foodstuffs and the most important export partners are Russia 9.9%, Egypt 6.2%, Poland 6.1%, Turkey 5.7%, Italy 5.3%, India 5.2%, China 5.1% (2016). The most important import commodities are energy, machinery and equipment, chemicals and the most important import partners are Russia 13.1%, China 12%, Germany 11%, Belarus 7.1%, Poland 6.9%, US 4.3% (2016). How rich is Ukraine and how rich are people in this country? The most important number here is GDP per capita (PPP): $8,700 (2017 est.). This is quite a low number. Let's add that this means Gross Domestic Product per person, which is recalculated with respect to the relative cost of local goods and services. And one more important number - population below poverty line: 24.1% (2010 est.).