World Atlas: Malaysia. On this page you can see the map, country flag and many detailed information about the people, history and economy of Malaysia.
Here you can find online selected information about the geography, inhabitants, government, economy and history of Malaysia. Included are selected statistics, an overview map and the detailed map of Malaysia. But let's start with the flag of Malaysia here:
Malaysia - Overview:
What you should know about Malaysia? Let's start with this: During the late 18th and 19th centuries, Great Britain established colonies and protectorates in the area of current Malaysia; these were occupied by Japan from 1942 to 1945. In 1948, the British-ruled territories on the Malay Peninsula except Singapore formed the Federation of Malaya, which became independent in 1957. Malaysia was formed in 1963 when the former British colonies of Singapore, as well as Sabah and Sarawak on the northern coast of Borneo, joined the Federation. The first several years of the country's independence were marred by a communist insurgency, Indonesian confrontation with Malaysia, Philippine claims to Sabah, and Singapore's withdrawal in 1965. During the 22-year term of Prime Minister Mahathir bin Mohamad (1981-2003), Malaysia was successful in diversifying its economy from dependence on exports of raw materials to the development of manufacturing, services, and tourism. Prime Minister Mohamed Najib bin Abdul Razak (in office since April 2009) has continued these pro-business policies.
Geography of Malaysia
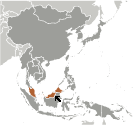 Where on the globe is Malaysia? The location of this country is Southeastern Asia, peninsula bordering Thailand and northern one-third of the island of Borneo, bordering Indonesia, Brunei, and the South China Sea, south of Vietnam. Total area of Malaysia is 329,847 sq km, of which 328,657 sq km is land. So this is quite a large country. How could we describe the terrain of the country? This way: coastal plains rising to hills and mountains. The lowest point of Malaysia is Indian Ocean 0 m, the highest point Gunung Kinabalu 4,095 m. And the climate is tropical; annual southwest (April to October) and northeast (October to February) monsoons.
Where on the globe is Malaysia? The location of this country is Southeastern Asia, peninsula bordering Thailand and northern one-third of the island of Borneo, bordering Indonesia, Brunei, and the South China Sea, south of Vietnam. Total area of Malaysia is 329,847 sq km, of which 328,657 sq km is land. So this is quite a large country. How could we describe the terrain of the country? This way: coastal plains rising to hills and mountains. The lowest point of Malaysia is Indian Ocean 0 m, the highest point Gunung Kinabalu 4,095 m. And the climate is tropical; annual southwest (April to October) and northeast (October to February) monsoons.
Inhabitants of Malaysia
Let's take a look how many people live in Malaysia. The number is: 31,381,992 (July 2017 est.). So quite a lot people live here. Who lives here? Bumiputera 61.7% (Malays and indigenous peoples, including Orang Asli, Dayak, Anak Negeri), Chinese 20.8%, Indian 6.2%, other 0.9%, non-citizens 10.4% (2017 est.). What are the languages in Malaysia? Bahasa Malaysia (official), English, Chinese (Cantonese, Mandarin, Hokkien, Hakka, Hainan, Foochow), Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, Panjabi, Thai. And the religions: Muslim (official) 61.3%, Buddhist 19.8%, Christian 9.2%, Hindu 6.3%, Confucianism, Taoism, other traditional Chinese religions 1.3%, other 0.4%, none 0.8%, unspecified 1% (2010 est.). How old are the people in average? 28.5 years. We have to add that this number is the median - so one half of the people is older than this, one half is younger. And what is their life expectancy (at birth)? This: 75.2 years. Where the people live in Malaysia? Here: a highly uneven distribution with over 80% of the population residing on the Malay Peninsula. The major urban areas of Malaysia are: Kuala Lumpur (capital) 6.837 million; Johor Bahru 912,000 (2015).
Government and Economy of Malaysia
The capital of Malaysia is Kuala Lumpur; note - nearby Putrajaya is referred to as a federal government administrative center but not the capital; Parliament meets in Kuala Lumpu and the government type federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy. Let's take a look at the administrative divisions - 13 states (negeri-negeri, singular - negeri); Johor, Kedah, Kelantan, Melaka, Negeri Sembilan, Pahang, Perak, Perlis, Pulau Pinang, Sabah, Sarawak, Selangor, Terengganu; and 1 federal territory (Wilayah Persekutuan) with 3 components, Kuala Lumpur, Labuan, and Putrajaya. Regarding the economy of Malaysia, important industrial products are Peninsular Malaysia - rubber and oil palm processing and manufacturing, petroleum and natural gas, light manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, medical technology, electronics and semiconductors, timber processing; Sabah - logging, petroleum and natural gas production; Sarawak - agriculture processing, petroleum and natural gas production, logging. Important agricultural products are Peninsular Malaysia - palm oil, rubber, cocoa, rice; Sabah - palm oil, subsistence crops; rubber, timber; Sarawak - palm oil, rubber, timber; peppe. The most important export commodities are semiconductors and electronic equipment, palm oil, petroleum and liquefied natural gas, wood and wood products, palm oil, rubber, textiles, chemicals, solar panels and the most important export partners are Singapore 14.7%, China 12.6%, US 10.3%, Japan 8.1%, Thailand 5.7%, Hong Kong 4.8%, India 4.1% (2016). The most important import commodities are electronics, machinery, petroleum products, plastics, vehicles, iron and steel products, chemicals and the most important import partners are China 19.4%, Singapore 9.8%, Japan 7.7%, US 7.6%, Thailand 5.8%, South Korea 5%, Indonesia 4% (2016). How rich is Malaysia and how rich are people in this country? The most important number here is GDP per capita (PPP): $28,900 (2017 est.). This means the living standards are good here. Let's add that this means Gross Domestic Product per person, which is recalculated with respect to the relative cost of local goods and services. And one more important number - population below poverty line: 3.8% (2009 est.).