World Atlas: Kosovo. On this page you can see the map, country flag and many detailed information about the people, history and economy of Kosovo.
Here you can find online selected information about the geography, inhabitants, government, economy and history of Kosovo. Included are selected statistics, an overview map and the detailed map of Kosovo. But let's start with the flag of Kosovo here:
Kosovo - Overview:
What you should know about Kosovo? Let's start with this: The central Balkans were part of the Roman and Byzantine Empires before ethnic Serbs migrated to the territories of modern Kosovo in the 7th century. During the medieval period, Kosovo became the center of a Serbian Empire and saw the construction of many important Serb religious sites, including many architecturally significant Serbian Orthodox monasteries. The defeat of Serbian forces at the Battle of Kosovo in 1389 led to five centuries of Ottoman rule during which large numbers of Turks and Albanians moved to Kosovo. By the end of the 19th century, Albanians replaced Serbs as the dominant ethnic group in Kosovo. Serbia reacquired control over the region from the Ottoman Empire during the First Balkan War of 1912. After World War II, Kosovo's present-day boundaries were established when Kosovo became an autonomous province of Serbia in the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (S.F.R.Y.). Despite legislative concessions, Albanian nationalism increased in the 1980s, which led to riots and calls for Kosovo's independence. The Serbs - many of whom viewed Kosovo as their cultural heartland - instituted a new constitution in 1989 revoking Kosovo's autonomous status. Kosovo's Albanian leaders responded in 1991 by organizing a referendum declaring Kosovo independent. Serbia undertook repressive measures against the Kosovar Albanians in the 1990s, provoking a Kosovar Albanian insurgency. Beginning in 1998, Serbia conducted a brutal counterinsurgency campaign that resulted in massacres and massive expulsions of ethnic Albanians (some 800,000 ethnic Albanians were forced from their homes in Kosovo). After international attempts to mediate the conflict failed, a three-month NATO military operation against Serbia beginning in March 1999 forced the Serbs to agree to withdraw their military and police forces from Kosovo. UN Security Council Resolution 1244 (1999) placed Kosovo under a transitional administration, the UN Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (Unmik), pending a determination of Kosovo's future status. A UN-led process began in late 2005 to determine Kosovo's final status. The 2006-07 negotiations ended without agreement between Belgrade and Pristina, though the UN issued a comprehensive report on Kosovo's final status that endorsed independence. On 17 February 2008, the Kosovo Assembly declared Kosovo independent. Since then, over 110 countries have recognized Kosovo, and it has joined numerous international organizations. In October 2008, Serbia sought an advisory opinion from the International Court of Justice (ICJ) on the legality under international law of Kosovo's declaration of independence. The ICJ released the advisory opinion in July 2010 affirming that Kosovo's declaration of independence did not violate general principles of international law, UN Security Council Resolution 1244, or the Constitutive Framework. The opinion was closely tailored to Kosovo's unique history and circumstances. Demonstrating Kosovo’s development into a sovereign, multi-ethnic, democratic country the international community ended the period of Supervised Independence in 2012. Elections were held throughout Kosovo in 2013 and 2014, at the municipal and national level respectively. Serbia continues to reject Kosovo's independence, but the two countries reached an agreement to normalize their relations in April 2013 through EU-facilitated talks and are currently engaged in the implementation process. Kosovo seeks full integration into the international community, and has pursued bilateral recognitions and eventual membership in international organizations, such as the UN, EU, and NATO.
Geography of Kosovo
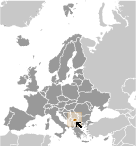 Where on the globe is Kosovo? The location of this country is Southeast Europe, between Serbia and Macedonia. Total area of Kosovo is 10,887 sq km, of which 10,887 sq km is land. So this is quite a small country. How could we describe the terrain of the country? This way: flat fluvial basin at an elevation of 400-700 m above sea level surrounded by several high mountain ranges with elevations of 2,000 to 2,500 m. The lowest point of Kosovo is Drini i Bardhe/Beli Drim 297 m (located on the border with Albania), the highest point Gjeravica/Deravica 2,656 m. And the climate is influenced by continental air masses resulting in relatively cold winters with heavy snowfall and hot, dry summers and autumns; Mediterranean and alpine influences create regional variation; maximum rainfall between October and Decembe.
Where on the globe is Kosovo? The location of this country is Southeast Europe, between Serbia and Macedonia. Total area of Kosovo is 10,887 sq km, of which 10,887 sq km is land. So this is quite a small country. How could we describe the terrain of the country? This way: flat fluvial basin at an elevation of 400-700 m above sea level surrounded by several high mountain ranges with elevations of 2,000 to 2,500 m. The lowest point of Kosovo is Drini i Bardhe/Beli Drim 297 m (located on the border with Albania), the highest point Gjeravica/Deravica 2,656 m. And the climate is influenced by continental air masses resulting in relatively cold winters with heavy snowfall and hot, dry summers and autumns; Mediterranean and alpine influences create regional variation; maximum rainfall between October and Decembe.
Inhabitants of Kosovo
Let's take a look how many people live in Kosovo. The number is: 1,895,250 (July 2017 est.). So not so many people live here. Who lives here? Albanians 92.9%, Bosniaks 1.6%, Serbs 1.5%, Turk 1.1%, Ashkali 0.9%, Egyptian 0.7%, Gorani 0.6%, Romani 0.5%, other/unspecified 0.2%. What are the languages in Kosovo? Albanian (official) 94.5%, Bosnian 1.7%, Serbian (official) 1.6%, Turkish 1.1%, other 0.9% (includes Romani), unspecified 0.1%. And the religions: Muslim 95.6%, Roman Catholic 2.2%, Orthodox 1.5%, other 0.07%, none 0.07%, unspecified 0.6% (2011 est.). How old are the people in average? 29.1 years. We have to add that this number is the median - so one half of the people is older than this, one half is younger. And what is their life expectancy (at birth)? This: unknown. Where the people live in Kosovo? Here: population clusters exist throughout the country, the largest being in the east in and around the capital of Pristina. The major urban areas of Kosovo are: Pristina (capital) 207,062 (2014).
Government and Economy of Kosovo
The capital of Kosovo is Pristina (Prishtine, Prishtina) and the government type parliamentary republic. Let's take a look at the administrative divisions - 38 municipalities (komunat, singular - komuna (Albanian); opstine, singular - opstina (Serbian)); Decan (Decani), Dragash (Dragas), Ferizaj (Urosevac), Fushe Kosove (Kosovo Polje), Gjakove (Dakovica), Gjilan (Gnjilane), Gllogovc (Glogovac), Gracanice (Gracanica), Hani i Elezit (Deneral Jankovic), Istog (Istok), Junik, Kacanik, Kamenice (Kamenica), Kline (Klina), Kllokot (Klokot), Leposaviq (Leposavic), Lipjan (Lipljan), Malisheve (Malisevo), Mamushe (Mamusa), Mitrovice e Jug (Juzna Mitrovica) [South Mitrovica], Mitrovice e Veriut (Severna Mitrovica) [North Mitrovica], Novoberde (Novo Brdo), Obiliq (Obilic), Partesh (Partes), Peje (Pec), Podujeve (Podujevo), Prishtine (Pristina), Prizren, Rahovec (Orahovac), Ranillug (Ranilug), Shterpce (Strpce), Shtime (Stimlje), Skenderaj (Srbica), Suhareke (Suva Reka), Viti (Vitina), Vushtrri (Vucitrn), Zubin Potok, Zvecan. Regarding the economy of Kosovo, important industrial products are mineral mining, construction materials, base metals, leather, machinery, appliances, foodstuffs and beverages, textiles. Important agricultural products are wheat, corn, berries, potatoes, peppers, fruit; dairy, livestock; fish. The most important export commodities are mining and processed metal products, scrap metals, leather products, machinery, appliances, prepared foodstuffs, beverages and tobacco, vegetable products, textiles and apparel and the most important export partners are Albania 24.2%, Macedonia, The Former Yugo Rep of 17.3%, Germany 8.8%, Switzerland 7.7%, Bulgaria 7.5%, Netherlands 6.9%, Turkey 4.6%, Austria 4.4% (2016). The most important import commodities are foodstuffs, livestock, wood, petroleum, chemicals, machinery, minerals, textiles, stone, ceramic and glass products, electrical equipment and the most important import partners are Macedonia, The Former Yugo Rep of 34.1%, Turkey 12%, Germany 9.4%, Albania 7.4%, Slovenia 6.9%, Italy 4.6% (2016). How rich is Kosovo and how rich are people in this country? The most important number here is GDP per capita (PPP): $10,400 (2017 est.). This is quite good. Let's add that this means Gross Domestic Product per person, which is recalculated with respect to the relative cost of local goods and services. And one more important number - population below poverty line: 30% (2013 est.).